Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom Notes
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom Notes:-
In this post, you will get the notes of B.com 3rd year money and financial system, by reading this post you can score well in the exam, hope that this post has helped you with this post to all your friends and all groups right now I must share it so that every student can read this post and it can also be helped in this post. Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
NON-BANKING FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Meaning of Non-Banking Financial Institutions
In every economy there are some financial intermediaries that are not like banks, but perform almost similar functions as the banks do. These intermediaries are called non-bank financial intermediaries (NBFIs). These intermediaries cannot create money or loanable funds, but they are simple brokers of loanable funds. Non-banking financial institutions are those companies which are not banking companies under the Banking Regulation Act and the Reserve Bank of India Act but carry out financial activities of providing finance.
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
These companies may or may not accept deposits from public, They provide lease finance housing finance, equipment finance. They trade in shares, provide general loans and advance for shares trading, hire purchase finance specially against automobiles. Financial intermediaries are dealers of financial claims. The claims issued by the NBFIs are called indirect securities or secondary securities which are more liquid than the direct securities or primary securities. The NBFIs receive primary securities from the ultimate borrowers and issue their own secondary securities to ultimate lenders.
The NBFIs are the instruments through which funds can move from lenders to borrowers. Commercial banks and NBFIs both these institutions have a common feature, i.e. both these institutions act as intermediaries between surplus units and the deficit units in the matter of transfer of funds. NBFIs include institutions such as life insurance companies, mutual saving bank, pension funds, hire purchase systems, investment trusts, etc. (Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom)
In the words of Gurley and Shaw, “The principal function of financial intermediaries is to purchase primary securities from ultimate borrowers and to issue indirect debt for the portfolio of ultimate lenders…. all financial intermediaries create financial assets.” Therefore, the basic function of NBFIs is to acquire less liquid assets and issue the more liquid liabilities of NBFIs, for which they charge a commission which is their income. Like commercial banks, NBFIs are also profit making institutions.
Types of NBFIs in India
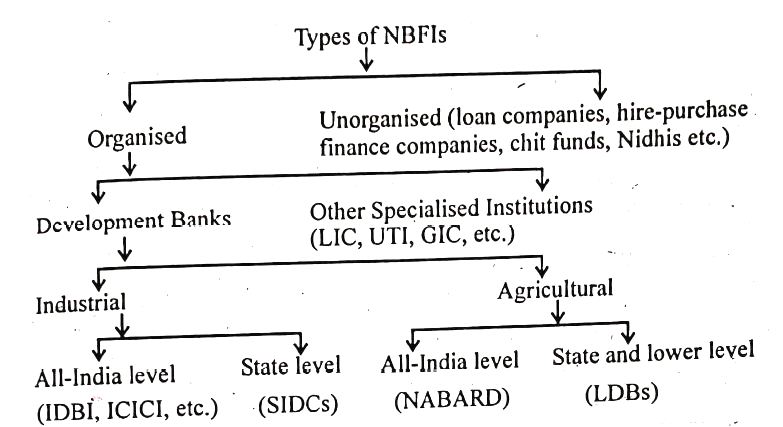
At present, various types of NBFIs are operating in India (as shown the following chart):
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
Broadly, NBFIs in India are classified into two groups: (a) organised NBFIs and (b) unorganised NBFIs.
- Organised NBFIs: The organised NBFIs include (i) development banks, and (ii) other specialised institutions. Development banks are those financial institutions which perform twin functions of providing medium and long term loans to the private entrepreneurs and of performing various promotional roles conducive to economic development. Development banks are further divided into (a) industrial development banks, such as, Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), (Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom) Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI), State Industrial Development Corporation (SIDC), etc.; and (b) agricultural development banks, such as, National Bank for Agriculture and Development (NABARD), Land Development Banks (LDBS). Some more NBFIs (other than development banks) operating in the organised sector are: Life Insurance Corporation (LIC), Unit Trust of India (UTI), General Insurance Corporation (GIC), etc.
- Unorganised NBFIS: A number of unorganised NBFIs also operate in the country. They are known as loan companies, hire-purchase financial companies, chit funds, nidhis, etc.
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
NBFIs are beneficial to the primary savers because of the following reasons:
(1) NBFIs reduce risk of savers: Lending to financial institutions is less risky because (a) the deposits are insured by regulatory agencies; and (b) the financial institutions gather many funds from many savers and relend these funds to many borrowers; thus the risk is spread over many types of loans and many different borrowers.
(ii) Secondary securities sold by financial intermediaries are easier to purchase, hold and sell. They are also economical because of low information and transaction costs.
(iii) Financial intermediaries provide sufficient liquidity on their secondary securities to their creditors.
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
(iv) It is true that indirect financial assets offer less liquidity than money in many cases, they can offer security, interest, yield and other services as well.
(v) Financial institutions can undertake credit analysis and investigation of the creditworthiness of the borrowers, such investigations are not possible by the individual lenders.
Distinction Between Commercial Banks and NBFIs
Inspite of certain similarities, the commercial banks basically differ from nonbank financial intermediaries on the following grounds:
(i) Bank is a financial institution whose liabilities (i.e., deposits) are widely accepted as a means of payment in the settlement of debt. Nonbank financial intermediaries, on the other hand, are those institutions whose liabilities are not accepted as means of payment for the settlement of debt.
(ii) Commercial banks have the ability to generate multiple expansion of credit. The non-bank inter-mediaries do not have such ability. They simply mobilise saving for investment.
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
(iii) The credit creation activities of the commercial banks are determined by the excess reserve and the cash-reserve ratio of the banks. The activities of the nonbank intermediaries (i.e., saving mobilisation, lending activities, etc.,) are largely governed by the structure of interest rates. (iv) Credit creation activities of the banks involve lesser time, while the lending activities of the nonbanks intermediaries involve longer time.
(v) The credit activities of the commercial banks are regulated and controlled by the central bank. The nonbank intermediaries are not generally under the control of central bank, and thus, their activities may create hurdles in the way of effective implementation of monetary policy.
(vi) Nonbank intermediaries can influence liquidity and create economic destabilisation in the economy. Destabilisation occurs when the financial claims on the nonbank intermediaries increase at the cost of demand deposits of the banks.
(vii) Commercial banks raise funds costlessly because no interest is paid on demand deposits. Nonbank intermediaries, on the other hand, have to pay bigher interest to attract more funds.
(viii) people deposit money in the banks for safety, convenience and liquidity consideration But, they invest their savings in the nonbank intermediaries with the motive of earning extra income.
Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
(ix) Banks from a homogeneous group, while nonbank intermediaries from a heterogeneous group in the financial structure of the economy.
(x) Bank generally deals with short-term loans in the money market, whereas the nonbank intermediaries mostly deal with all types of loans, i.e., short-term, medium-term and long-term loans.

Non Banking Financial Institutions Bcom
 |
|||